What is Git? And How to Use It to Manage Your Project’s Versions
Greetings and welcome back to my humble blog, dear beautiful reader! We’ve returned with a new article after a long absence. This time, we’ll talk about a very important topic for every programmer: Git. In simple terms, for those unfamiliar, it is a program we use to manage projects and their versions. It’s most commonly used alongside repository hosting sites like:
- Github
- Gitlab
There are many repository hosting platforms, but in this article, we won’t discuss “Github” or how to publish your repository on it, since that would be a lengthy subject! Instead, I’ve decided to split the article into two parts:
- Part One: Explaining the basics of Git and how to use it locally.
- Part Two: Explaining Github and how to publish your projects there.
Let’s begin…
Initializing Your Project Folder as a Local Repository
- To initialize your folder as a local Git repository, you need to run the following command inside the folder:
git init .The dot at the end means the current directory, so we’re telling Git to initialize the current folder as a local repository.
- To add all the files in your folder, enter:
git add .- If there are files or folders you’d like to exclude, meaning they won’t be added to your local repository, create a file named:
touch .gitignoreIt’s best to create this before adding files in the previous step.
Next, open the file in your favorite text editor, for example, neovim, and enter the names of the folders and files you want ignored:
# Folders
bin/
# Files
config.bak- Now, for the final step, you save your changes by making a commit:
git commit -m "commit message"The “-m” in the previous command is a flag for the commit message — a quick explanation of what was added or changed.
After you’ve run all the above commands, it should look something like this:
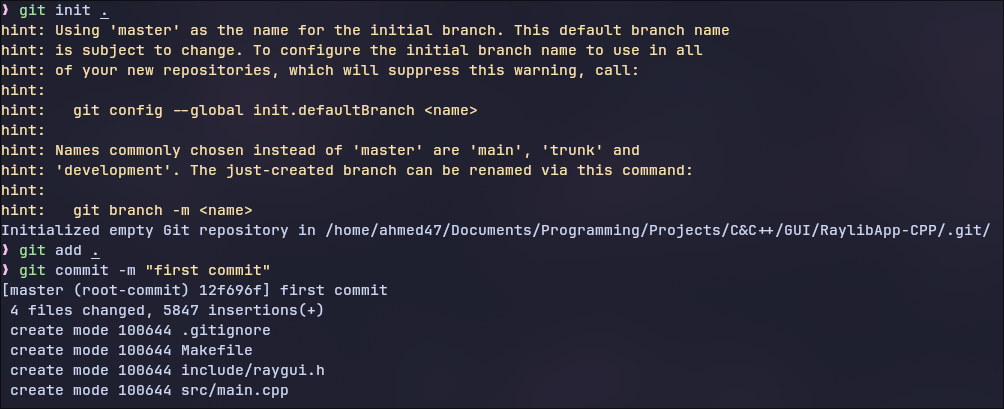
Reverting Specific Changes
Suppose you added some lines to your project that caused problems. How can you undo those changes and restore the last correct version? Simply use the following command:
git restore .This command will remove any modifications you made after the last commit.
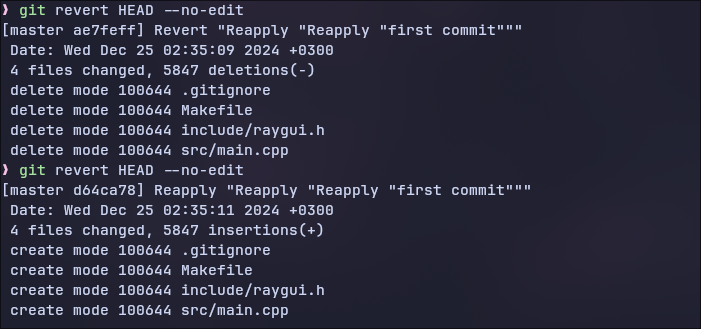
But what if you performed a commit and only then discovered a problem that broke your project? You can undo the most recent commit with:
git revert HEAD --no-editHere’s an image showing the process:
Conclusion
Finally, thank you so much, dear sweet reader, for reaching the end of this blog post. I hope you enjoyed it, and until we meet again, I wish you well and good health! Goodbye 🖤.